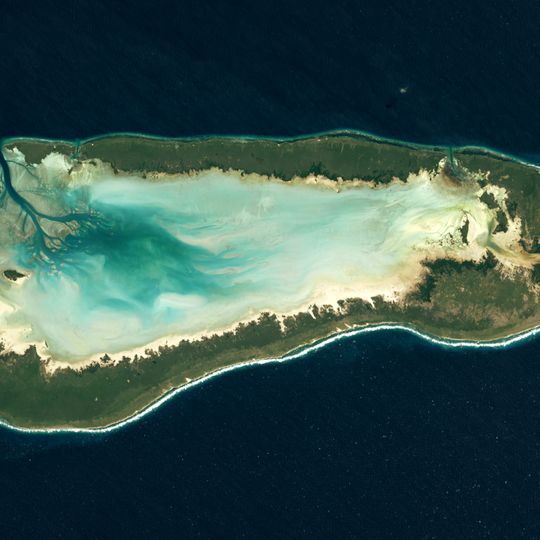
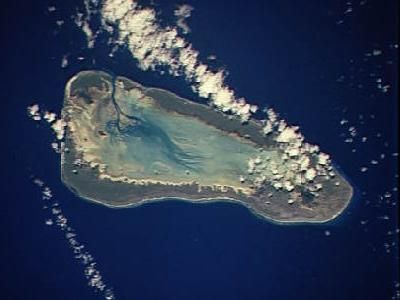
Aldabra, UNESCO World Heritage Site atoll in Seychelles.
Aldabra is an atoll in the Indian Ocean made up of four main islands surrounding a central lagoon filled with coral reefs, mangrove forests, and seagrass beds. The shallow waters and remote location have created a self-contained world where life has developed in ways found nowhere else.
Arab sailors first found this coral atoll, and it later fell under French control during the 1700s before passing to British rule in 1810. Eventually it became part of the Seychelles following the nation's independence.
The atoll functions as a natural laboratory where scientists conduct research on island ecosystems, contributing to global conservation knowledge.
Getting there requires special permits and must be arranged through authorized operators due to strict environmental rules. Visitors should expect limited facilities and rough conditions typical of a remote protected nature reserve.
The atoll is home to the largest population of giant tortoises in the region, animals that live for many decades and shape the character of the islands. These creatures are found almost nowhere else on Earth, making this place their most important refuge.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.