US Coast Guard and Geodetic Survey Seismological and Geomagnetic House, Scientific observation building in Sitka, United States.
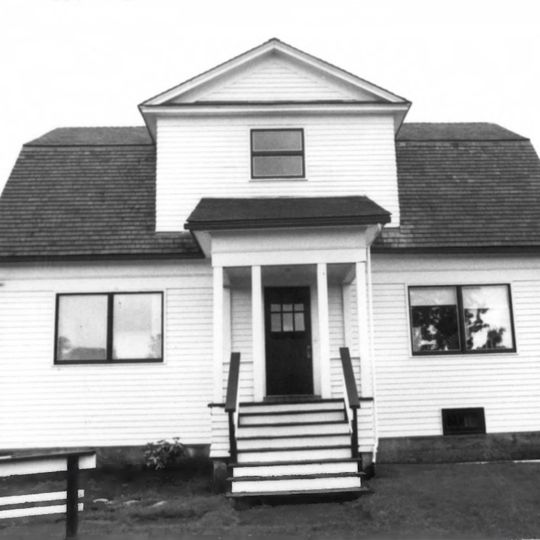
The US Coast Guard and Geodetic Survey Seismological and Geomagnetic House at 210 Seward Street is a two-story wood-sided structure with a gambrel roof design. It contains seven rooms arranged with three bedrooms upstairs and scientific workspaces below, featuring a concrete basement set directly into bedrock for stability and instrument protection.
Built in 1916 by the United States Department of Commerce, it operated as the first permanent geomagnetic observatory in Alaska through 1940. The facility supported early scientific research into Earth's magnetic properties from this remote northern location.
The site once hosted the Russian Tea Garden, a remnant from when Russia controlled the territory before ceding Alaska to the United States in 1867. This location marks a transition point between two colonial periods in the town's history.
The building sits on solid bedrock, which provides a stable foundation visible in its basement construction and important for understanding the site's scientific purpose. The location on Seward Street is easily accessible, and the exterior wood and roof details are clearly visible when walking past the structure.
The site was selected specifically because the absence of local magnetic disturbances allowed precise measurements of Earth's magnetic field. This geographical advantage made Sitka one of the few locations where such sensitive research could be conducted reliably during that era.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.