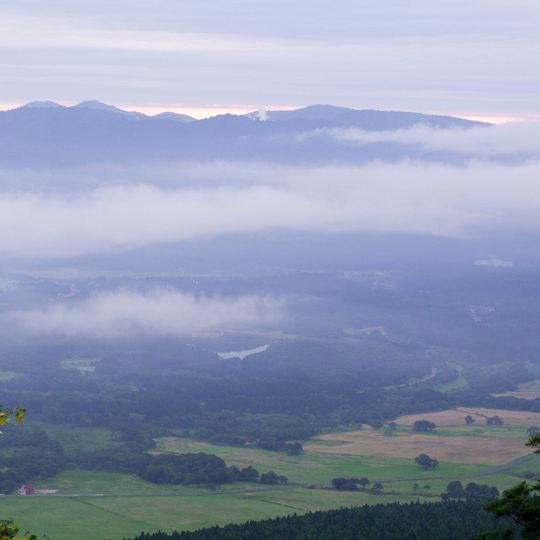
Onikōbe Caldera, Volcanic caldera in Osaki, Japan.
Onikōbe Caldera is a volcanic depression spreading across multiple regions at an elevation of 769 meters. The terrain features numerous steam vents and hot springs that result from ongoing geothermal activity in the area.
The caldera formed through repeated volcanic eruptions spanning thousands of years, which gradually caused the ground to collapse. This geological transformation shaped how the landscape developed and influenced human settlement patterns in the region.
The communities surrounding the caldera have adapted to geothermal activity for generations, using hot springs as places for bathing and healing. The volcanic landscape remains central to how local people understand and relate to their environment.
The site is reachable by public transportation from major cities, with several trails available for exploring the area. Visitors should prepare for uneven ground and weather that can change quickly in mountainous terrain.
The caldera continuously supplies hot water to multiple thermal facilities throughout the year from deep underground sources. This constant geothermal energy allows local establishments to maintain traditional bathing experiences year-round.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.