Parinacota, Dormant stratovolcano in Oruro Province, Bolivia
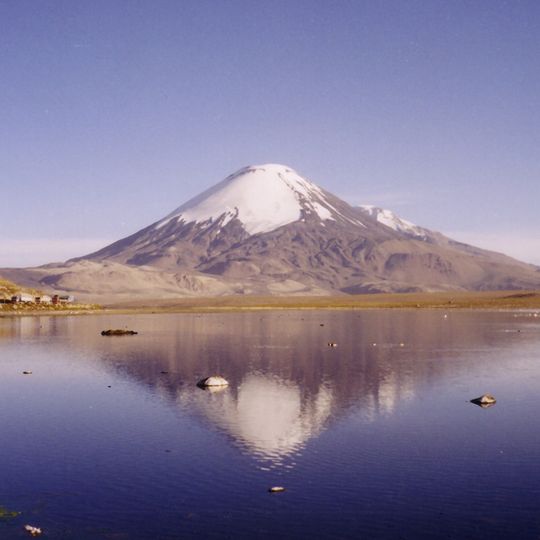
Parinacota is a dormant stratovolcano in Oruro Province, Bolivia, standing at 6,380 meters in elevation. The mountain displays a symmetrical cone shape with a crater spanning roughly 1 kilometer across at its summit.
The volcano formed during the transition from the Pleistocene to the Holocene epoch, when its western flank collapsed catastrophically. This collapse generated a massive landslide that created Lake Chungará below.
The name comes from the Aymara language, where 'parina' means flamingo and 'quta' means lake. This reflects the indigenous roots of the communities living in the high plains around the volcano.
The mountain can be climbed with local guides from Sajama village, with multi-day climbing expeditions available. The best climbing season is during the drier months when weather conditions are more stable.
Three parasitic cones called Ajata dot the southern slopes and produced distinct lava flows across the landscape. These smaller volcanic features reveal a more complex volcanic story than the main cone alone suggests.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.