Khirbet Qeiyafa, Archaeological site in Elah Valley, Israel
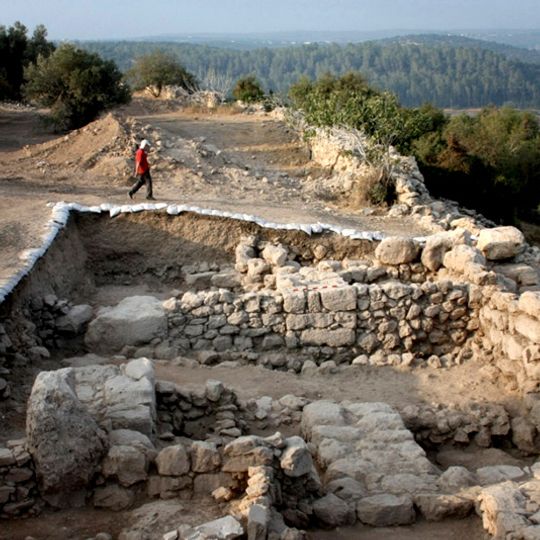
Khirbet Qeiyafa is a fortified Iron Age settlement in the Elah Valley of Israel, roughly 19 miles (30 kilometers) southwest of Jerusalem. The site consists of massive stone walls enclosing a nearly oval area, with rectangular building remains inside that once served as living quarters and storage rooms.
The settlement was founded in the 10th century BCE and occupied for only a few decades before being abandoned. Excavations starting in 2007 uncovered pottery shards and other artifacts linking the site to early kingdoms in southern Canaan.
The name Sha'arayim comes from the Hebrew word for gates and refers to the double entryways in the city wall. Visitors today can see the foundations of these two passages and trace how defenders used the layout to control access.
The site sits on a hilltop with open views over the valley, so sturdy footwear is helpful for uneven paths. Information panels stand at key points and explain the function and layout of the exposed structures in several languages.
Researchers found a clay shard here inscribed with what may be the oldest known Hebrew text, containing words like king and slave. The discovery sparked debates about early literacy in the region and shows that writing was already in use around 3000 years ago.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.