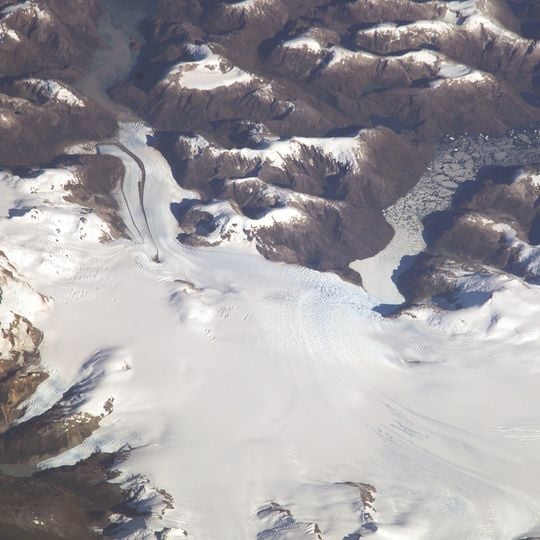
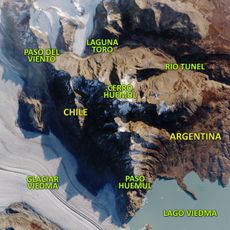
Aguilera, Stratovolcano in Southern Patagonia, Chile.
Aguilera is a stratovolcano in the southern Andes that rises 2,546 meters above the Patagonian Ice Field. It forms part of a volcanic group of six peaks that make up the southernmost section of the Andean Volcanic Zone.
The volcano remained unknown until 1985 when geological surveys confirmed its volcanic nature. Its first successful ascent took place in 2014, opening it to human exploration.
The volcano shaped how people understood settlement patterns in remote Patagonia, with volcanic deposits marking early human sites across the region. Visitors can observe these environmental traces in the surrounding landscape today.
Conditions here are harsh year-round, with temperatures ranging from 4 to 10 degrees Celsius and strong western winds. Visitors should prepare for intense weather and bring appropriate gear.
A major past eruption dispersed volcanic material across the entire Patagonian region and reached the Strait of Magellan. This scale of activity reveals the immense power of this southernmost volcano.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.