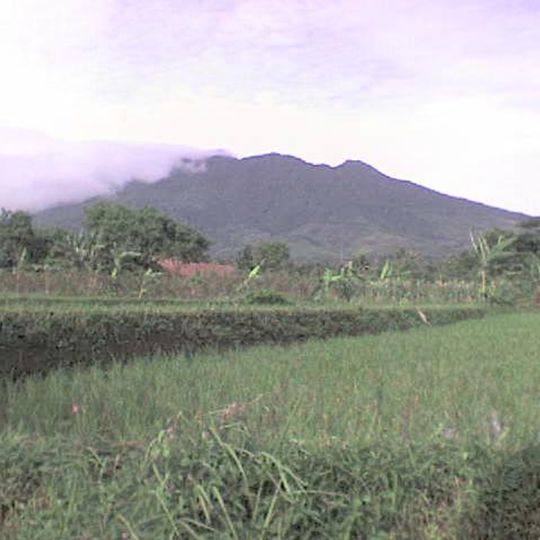
Mount Salak, Stratovolcano in West Java, Indonesia.
Mount Salak is a stratovolcano in Bogor rising 2,211 meters above sea level with several smaller satellite cones along its southeastern slope. Two additional craters open at the summit and give the top a double shape visible from below.
Between 1780 and 1938 five eruptions occurred, all taking place at flank vents and classified as phreatic eruptions. This type of activity arises from contact between magma and groundwater and leaves no large lava flows.
The name comes from a Sanskrit word for silver and appears today on road signs and shop fronts around the base of the volcano. Hikers encounter the term regularly on orientation boards along the trails that lead to the top and pass by small settlements.
The Curug Nangka route on the northern side leads to the summit and offers water sources until the Post III shelter for hikers. The ascent can become slippery during rain, so sturdy footwear and a check on the weather before starting are worthwhile.
The volcano forms a water divide between two large river systems and directs tributaries toward both the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean. This geographic role makes it a natural hub for the hydrological network of the region.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.