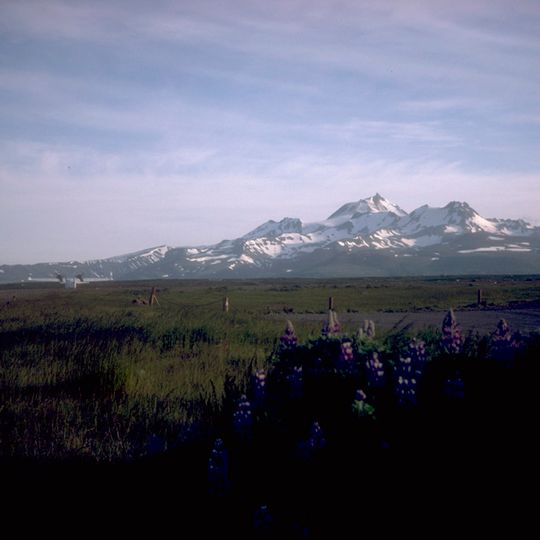
Cold Bay Volcano, Stratovolcano in Alaska Peninsula, United States.
Cold Bay Volcano is a stratovolcano on Alaska Peninsula featuring a cone-shaped structure rising to approximately 1,920 meters (6,299 feet) built from successive layers of lava and ash. The formation displays a double-cone pattern, with the northern section connected to Morzhovoi Volcano, which contains a collapsed caldera.
The volcano formed during the Pleistocene epoch through repeated eruptive cycles, with the southern cone established before Wisconsin Glaciation affected the region. The northern component featuring Morzhovoi developed as a later phase of this volcanic activity.
Native communities near Cold Bay developed methods to monitor volcanic activity through generations of observation and experience with the mountain's patterns.
Reaching this volcano requires helicopter or boat transport, as the remote location sits far from any paved roads. Visitors should prepare for harsh weather conditions and challenging terrain.
The peaks within the collapsed Morzhovoi caldera carry traditional animal names such as North Walrus and South Walrus, reflecting local knowledge of the region's marine wildlife. These geographic names reveal how volcanic features became tied to the surrounding ecosystem.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.