Abu Gorab, Solar temple ruins in Giza Governorate, Egypt.
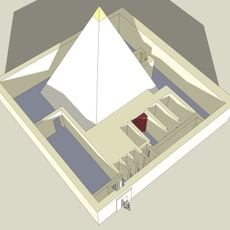
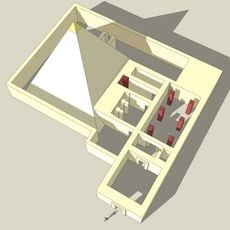
Abu Gorab is an archaeological site containing the remains of a sun temple with a large stone obelisk, alabaster basins, and limestone structures. The complex sits on the western bank of the Nile and reveals the typical layout of temples from the early pharaonic period.
This sun temple was built around 2400 BCE during the Fifth Dynasty by Pharaoh Nyuserre Ini and functioned as a religious center devoted to the sun god. The site demonstrates important developments in temple design and religious practices of that period.
The temple walls show carved reliefs that depict how ancient Egyptians honored their gods and the central place the sun god held in their beliefs. These images offer visitors a glimpse into what was sacred to these people long ago.
The site sits roughly 15 kilometers south of Cairo, positioned between Saqqara and Giza, and is best visited in the early morning to escape the intense desert heat. Sturdy footwear and sun protection are essential, as the area offers little shade.
Nine circular alabaster basins line the eastern wall of the temple courtyard, their exact purpose in ancient rituals remaining a matter of interpretation among scholars. These carefully crafted vessels are among the best-preserved examples of their kind.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.