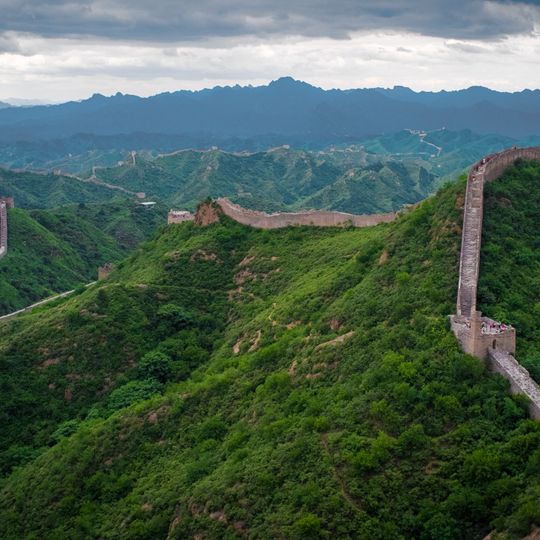
Great Wall of China, Fortified line across northern China spanning over 21,000 kilometers through multiple provinces.
This defense network consists of interconnected fortifications made from limestone, rammed earth, bricks, and stone that stretch across mountains, deserts, and plains. Watchtowers rise at intervals along ridges, with walls of varying height and width that follow the terrain, leaving many sections today in different states of preservation.
Early sections appeared around 700 BC under separate Chinese states, before Qin Shi Huangdi connected them into a unified system during the Qin Dynasty. Major expansion took place during the Ming Dynasty between 1368 and 1644, when most of the stone structures visible today were built.
Visitors observe people walking on the ramparts, flying kites, and photographing groups in traditional clothing, while vendors offer calligraphy and souvenirs nearby. Families gather on weekends to climb the steps together and enjoy the view, treating the monument as a place of personal connection to the past.
Popular sections like Badaling and Mutianyu open daily in the morning and close in late afternoon, with hours varying by season. Sturdy footwear is important because the steps are steep and uneven, and most visitors need two to three hours for a walk through.
Contrary to common claims, it is not visible from the Moon with the naked eye, and its construction relied on sticky rice mortar made from rice soup and lime to hold bricks together. Many sections run through remote areas that few tourists reach, with vegetation slowly growing over abandoned parts.
The community of curious travelers
AroundUs brings together thousands of curated places, local tips, and hidden gems, enriched daily by 60,000 contributors worldwide.